Transient Cavitation Models
AFT Impulse has two cavitation models available to capture transient cavitation in pipes: the Discrete Vapor Cavity Model (DVCM) and the Discrete Gas Cavity Model (DGCM).
Any cavitation in a system inherently violates AFT Impulse’s fundamental assumption that all pipes are 100% liquid-full. The cavitation models attempt to work around that assumption by modeling cavitation only at pipe computation stations, with the intervening pipe remaining liquid-full.
In a real system, vapor pockets can form continuously in the liquid. However, Impulse lumps all vapor formed into discrete pockets fixed at the grid points determined by the Method of Characteristics (MOC). Vapor volume is tracked at each station, and the MOC equations are applied to the pipe between each station following the liquid-full assumption.
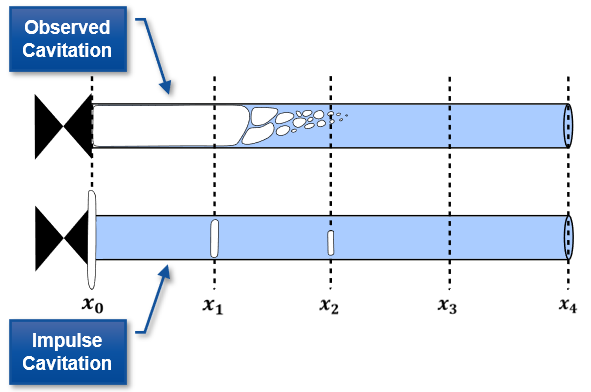
Figure 1: While observed cavitation occurs over a given pipe volume, AFT Impulse calculates vapor volumes at pipe stations
Both models, DVCM and DGCM, are based on the methodology described in Wylie, et al, 1993Wylie, E.B., V.L. Streeter & L. Suo, Fluid Transients in Systems, Prentice Hall, Englewood Hills, New Jersey, 1993., pg 66-69 (DVCM) and pg 184-187 (DGCM), and supplemented by other literature sources. These models are considered industry standard, and are considered good models for transient cavitation. However, their accuracy is inherently limited by the liquid-full assumption behind AFT Impulse and the MOC. See the Interpreting Transient Cavitation Predictions page.
Vapor Pressure Treated as a Stagnation Pressure
Pstag = Pstatic + Pdynamic (more info)
Vapor pressure is a thermodynamic property and thus represents the static pressure at which the liquid starts to vaporize. In theory, a cavitation model should treat vapor pressure as a static pressure. In practice, it is far easier to treat vapor pressure as a stagnation pressure because AFT Impulse solves the MOC using stagnation pressure (static pressure is back-calculated using velocity). Complex junction calculations simplify substantially when using stagnation pressure.
In a liquid-full pipe we can easily relate static and stagnation pressures because we know the velocity. When gas or vapor is present, calculating velocity to relate static and stagnation pressure becomes more difficult: 1) we do not know the gas velocity or the cross-sectional area it takes up, and 2) we do not know how the liquid cross-sectional area changes. Therefore, during cavitation we must either: 1) assume the liquid area is equal to the pipe area, or 2) assume the dynamic pressure is negligible.
AFT Impulse treats vapor pressure as a stagnation pressure for both DVCM and DGCM.
-
DVCM vapor volumes start to form when Pstag = Pvap
-
DGCM will see free gas expansion before Pstag reaches Pvap, then vaporization and cavitation when Pstag = Pvap
With DVCM the user can choose to treat Pvap as a static pressure via an option in the Waterhammer section of the User Options. DGCM cannot treat Pvap as a static pressure. AFT experience suggests that treating Pvap as a stagnation pressure matches empirical data better.
Discrete Vapor Cavity Model (DVCM)
DVCM evaluates transient cavitation by assuming one of two conditions exists. Either the pressure at the pipe computation station is greater than Pvapor and the MOC equations can be applied as normal, or the pressure at the pipe computation station is equal to Pvapor and cavitation is present.
When the MOC equations calculate that the pressure at a station reaches (or falls below) Pvapor, the pressure at that station is fixed exactly at Pvapor. The MOC equations are then evaluated treating the station as a boundary condition, simplifying the compatibility equations for the flowrate upstream and downstream of the station to:
Asserting a fixed pressure boundary of Pvapor creates a mass flow discontinuity across the station. Impulse assumes this mass flow discontinuity is caused by vapor pockets forming and tracks it as the total vapor volume. The actual mass flowrate as a function of time is unknown, so an average of the mass flowrate at the old time step and new time step is used:
When the vapor volume tracked at a station reaches (or falls below) zero, the station returns to the normal MOC equations.
Discrete Gas Cavity Model (DGCM)
DGCM builds on DVCM by introducing a small amount of free gas into the system. Most liquid systems contain some small amount of gas flowing with the liquid or dissolved in the liquid. This gas expands as system pressure approaches vapor pressure and can be considered a precursor to the cavitation which exists when the liquid is at vapor pressure.
Similar to DVCM, DGCM evaluates transient cavitation by assuming one of two conditions exists: either the station stagnation pressure is above Pvapor, or the system pressure is equal to Pvapor.
Calculations when Pstag > Pvapor:
When the station stagnation pressure is above Pvapor, DGCM uses the Ideal Gas Law to determine the free gas volume:
Specifically, nRT are lumped together as a constant value determined by the Initial Void Fraction and Initial Void Fraction Reference Pressure parameters on the Transient Cavitation Panel such that:
Impulse then couples the above equation with the MOC compatibility equations to simultaneously solve for the pressure, upstream mass flow rate, and downstream mass flowrate at each station for each time step. These calculations are always performed regardless of how close the system is to Pvap, adding additional computational complexity. As a result, a simulation using DGCM will take longer to run than a simulation using DVCM.
The free gas volume calculated at each station allows DGCM to improve on DVCM. Specifically, it allows DGCM to capture the effect that gas or vapor in a liquid system has on wavespeed. Wavespeed depends on how compressible a fluid is, with gas being more compressible than a liquid. At low pressures, gas volume will increase relative to the liquid, lowering the wavespeed in the fluid. This effect can become more pronounced as the fluid approaches the vapor pressure of the liquid, and is an important effect to capture.
The Method of Characteristics solution requires wavespeed to be fixed prior to the simulation, meaning wavespeed can’t be directly modified. However, DGCM forces a pressure wave to expend some energy compressing the gas volume at a station as the wave travels along the pipe, effectively slowing wave motion as gas volume increases at low pressures.
The small gas volume at each station also helps avoid some of the numerical noise associated with DVCM, effectively dampening high-frequency waves as they move through the system.
Note that the free gas in the system can be set using the Initial Void Fraction and Reference Pressure settings in the Transient Cavitation Panel. Default values are 1E-7 and 1 atm, respectively. Literature discussing DGCM, and AFT’s internal tests show that these values are meant to be constants rather than measured system values. AFT does not recommend changing these values from the default.
Calculations when Pstag = Pvapor:
When the station stagnation pressure is equal to Pvapor, DGCM simplifies to DVCM. The pressure at the station is fixed exactly at Pvapor, the MOC equations are evaluated treating that station as a boundary condition, and vapor volume is tracked as the mass flow discontinuity across the station.
DGCM contains one further difference from DVCM, seen in the equation used to integrate the mass flow discontinuity. DVCM integrates the total change in vapor volume from one time step to the next by averaging the mass flow evenly between the old time step and the new time step. DGCM instead uses rectangular integration and a weighting factor, ψ, with a value of 0.95, as shown in the equation below.
Using a value of ψ=0.95 weights the equation towards the new time step, adding numerical stability to the results, and providing a better match between Impulse results and available reference data. AFT does not recommend changing this value from the default.



