Gas Accumulator Waterhammer Theory
A gas accumulator (shown in Figure 1) is an enclosed tank filled with gas and has a free surface. It is used as a surge suppressor (Wylie, et al., 1993, pp. 125-128Wylie, E.B., V.L. Streeter & L. Suo, Fluid Transients in Systems, Prentice Hall, Englewood Hills, New Jersey, 1993.).The flow balance on the accumulator junction is similar to a branch junction, with the deficit equaling the flow out of the accumulator, ṁA.
Similar to a branch, it can be shown that for all connecting pipes to the junction,
where SC and SB are given by Equation 2 and Equation 3
from Branch Waterhammer Theory. The potential connector pipe and orifice effect is incorporated by the lumped inertia relationship as follows
where C1 and C2 are defined in conjunction with lumped inertia. Refer to and Equation 2
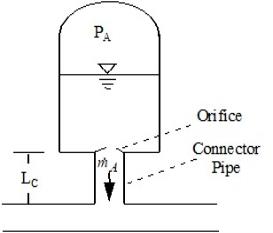
Figure 1: Gas accumulator schematic
The gas volume and pressure in the accumulator can be related by the thermodynamic law
where n is the polytropic constant (1.4 for isentropic air, 1.0 for isothermal) and CA is a constant.
Therefore,
and
By substitution
or
Combining equations and simplifying,
where
This is a non-linear equation that can be solved using Newton-Raphson iteration. Newton-Raphson has the following form:
where xi is the current value of x, xi+1 is the new value, F is the function of x to drive to zero, and F´ is the derivative.
In this case
When the value of ṁA,new has been found that causes F to equal zero, the equation will be satisfied. To solve by Newton-Raphson the derivative of F is given by,
where
By iteration, ṁA,new is calculated. This value can then be back-substituted to obtain the new junction pressure and new gas volume.
Gas Accumulator Vapor Cavitation Theory
Any short-lived vapor cavities that develop at a Gas Accumulator junction are assumed to have a negligible effect compared to the accumulator itself. Conceptually, vapor bubbles would rise by buoyancy to the accumulator surface and evaporate into the accumulator gas. Their effect on the system would thus be negligible compared to that of the accumulator gas. Therefore, vapor cavitation is ignored at gas accumulators.
Related Topics
Related Examples



