Importing From Excel
A Microsoft Excel spreadsheet can be used to make changes to objects in an AFT Impulse model. The values in the Excel file are located in specific locations as described in the Setting Up Excel section.
Setting Up Excel
When reading an Excel file, AFT Impulse will search for a worksheet named AFT Transfer. There can be other worksheets in the workbook but Impulse will only look for a sheet with this name. The file structure looks like the following:
The changes are entered on a worksheet named "AFT Transfer". There can be other worksheets in the workbook but Impulse will only look for a sheet with this name. The first data is entered in cell B2. Column A and row 1 are not read and are available for user comments. The file structure looks like the following:
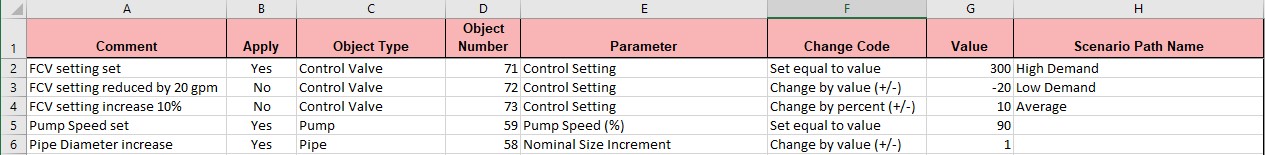
Figure 1: Sample AFT Transfer Excel Sheet
Row 1 and column A are not read by AFT Impulse - these cells can have any value in them, though it is recommended to enter the values above for the header row.
Each column has certain accepted values, which can depend on the values in neighboring columns.
Note: A template spreadsheet containing validation rules for the required layout is included in the AFT Impulse installation, or can be downloaded here. By default the file path is: C:\AFT Products\AFT Impulse\AFT Impulse Excel Import Workbook.xlsx.
Apply Column
This column accepts Yes or No. Only changes marked as Yes will be imported into the model.
Object Type
This column must be a junction name or Pipe. Valid choices can be seen below in Table 1.
Object Number
This corresponds to the junction or pipe number of the object being changed.
Parameter
The specific parameter to be changed. These parameters vary based on the Object Name selected. Each parameter has a type (C/S/I) associated with it, as is explained in the next section.
Table 1 - Object Types, Associated Parameters, and Change Codes
|
Pipe S Additional K Factor S Design Factor - Pipe Fittings & Losses S Design Factor - Pipe Friction S ID Reduction (Scaling) S Initial Flow Guess S Inner Diameter (for unspecified, cylindirical pipes) S Length S Modulus of Elasticity (for unspecified, cylindrical pipes) I Nominal Size Increment C Nominal Size Set (must match text in Pipe Property Window) C Nominal Type Set (must match text in Pipe Property Window) C Pipe Name S Poisson Ratio S Roughness Value I Special Condition S User Specified Wavespeed S Wall Thickness (for unspecified, cylindrical pipes) |
Area Change S Design Factor S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S Outlet Elevation S User Specified K |
Assigned Flow S Design Factor S Elevation S Flow Rate S Flow Temperature S Initial Guess Pressure C Junction Name I Special Condition |
Assigned Pressure S Design Factor S Elevation C Junction Name S Pressure |
Bend S Design Factor S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S Loss Model S Outlet Elevation I Special Condition S User Specified K |
|
Branch S Design Factor S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S Outlet Elevation S Source/Sink Flow |
Check Valve S Deceleration Calculation Interval (Estimated Fluid Velocity) S Delta Pressure/Head to Reopen (User Specified) S Design Factor S Disk/Plug Area (Force Balance) S Disk/Plug Submerged Weight (Force Balance) S Disk Distance to CG (Force Balance) S Disk Inertia (Force Balance) S Forward Velocity to Close Valve (User Specified) S Full Open Loss Value S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S Min Velocity Required to Fully Open (Vo) (Estimated Fluid Velocity) S Outlet Elevation S Plug Max Travel Length (Force Balance) I Special Condition S Spring Constant (Force Balance) S Spring Force with Valve Closed (Force Balance, Translating) S Spring Torque with Valve Closed (Force Balance, Spring) |
Control Valve S Design Factor S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S Loss When Fully Open S Outlet Elevation S Setpoint I Special Condition |
Dead End S Initial Guess Pressure S Elevation C Junction Name |
General Component S Design Factor S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S K Factor S Outlet Elevation I Special Condition |
|
Gas Accumulator S Design Factor S Initial Gas Volume S Initial Guess Pressure S Junction Elevation C Junction Name S Maximum Gas Volume S Minimum Gas Volume S Polytropic Constant in Transient S Precharge Gas Pressure S Precharge Gas Temperature S Precharge Gas Volume I Special Condition S Tank Diameter S Tank Height S Tank Length S Tank Volume |
Liquid Accumulator S Elasticity S Elevation S Initial Guess Pressure S Initial Volume C Junction Name I Special Condition |
Orifice S Area/Diameter S Design Factor S Exit Pressure S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S Loss Value S Outlet Elevation |
Pump S Control Setpoint S Delta Pressure to Re-Open Combined Check Valve S Design Factor S Fixed Speed (%) S Forward Velocity to Close Combined Check Valve S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name I Number of Heads (positive displacement) S Operating Speed (positive displacement) S Outlet Elevation S Rated Pump Speed (rpm) I Special Condition S Steady/Average Flow Rate (positive displacement) S Submerged Suction Pressure S Trimmed Impeller Ratio as Percent |
Relief Valve S Blowdown Pressure S Design Factor S Exit Pressure/Head S Initial Guess Pressure S Initial Elevation C Junction Name S Loss Value S Outlet Elevation S Remote High Pressure S Remote Low Pressure S Set Pressure I Special Condition |
|
Reservoir S Cross-sectional Area S Design Factor C Junction Name S Liquid Surface Elevation S Liquid Surface Pressure I Surface Elevation Type S Tank Bottom Elevation |
Screen S Design Factor S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S K Factor S Outlet Elevation |
Spray Discharge S Design Factor S Discharge Flow Area S Elevation S Exit Pressure S Initial Guess Pressure C Junction Name S Loss Value I Number of Holes I Special Condition |
Surge Tank S Cross-Sectional Area S Initial Guess Pressure C Junction Name I Special Condition S Surface Pressure |
Tee or Wye S Design Factor S Initial Guess Pressure S Elevation C Junction Name |
|
Turbine S Design Factor S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S Outlet Elevation I Special Condition |
Air Valve S Inlet Cracking Pressure S Gas External Pressure S Initial Gas Mass In System S Intermediate Orifice Activation Value S Elevation S Initial Guess Pressure C Junction Name S Outlet Elevation S Full Open Orifice CdA Inflow S Full Open Orifice CdA Outflow S Full Open Orifice CdA Intermediate Outflow I Special Condition |
Valve S Design Factor S Exit Pressure S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S Open Percentage S Outlet Elevation I Special Condition |
Venturi S Design Factor S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S Loss Value S Outlet Elevation |
Volume Balance S Initial Guess Pressure S Elevation C Junction Name |
|
Weir S Channel Width S Downstream Bottom Elevation S Downstream Cross-Sectional Area S Initial Guess Pressure S Inlet Elevation C Junction Name S Notch Width S Outlet Elevation I Special Condition S Surface Pressure S Upstream Bottom Elevation S Upstream Cross-Sectional Area S Height of Weir I Weir Type |
Change Code
Each Parameter has restrictions on how it can be changed. All of the Parameters are decimal numbers, integers, or strings.
Table 2: Valid Change Codes for each type of Parameter
|
Decimal Number (S) |
Integer Number (I) |
String (C) |
|
Set equal to value |
Set equal to value |
Set equal to value |
|
Change by value (+/-) |
Change by value (+/-) |
Add string to list |
|
Change by percent (+/-) |
Delete string from list |
Value
The actual value to change the Parameter to or by.
For special conditions there are specific values assigned to each special condition option, as are listed in the table below.
Table 3: Values used to import special conditions
|
Junction |
Special Condition |
Value |
|
Assigned Flow |
None Closed |
0 1 |
|
Check Valve |
None Closed Open |
0 1 2 |
|
Control Valve |
None Closed Fully Open - No Control |
0 1 2 |
|
Gas Accumulator |
None Ignore Accumulator |
0 5 |
|
General Component |
None Closed |
0 1 |
|
Liquid Accumulator |
None Ignore Accumulator |
0 5 |
|
Pump |
None Pump Off No Flow Pump Off With Flow Through |
0 1 2 |
|
Relief Valve |
None Failed Open Ignore Relief Valve |
0 2 5 |
|
Surge Tank |
None Ignore Surge Tank |
0 5 |
|
Spray Discharge |
None Closed |
0 1 |
|
Turbine |
None Closed |
0 1 |
|
Air Valve |
None Ignore Air Valve |
0 5 |
|
Valve |
None Closed |
0 1 |
|
Weir |
None Ignore Weir |
0 5 |
Scenario Path Name
The Scenario that the changes are intended to apply to. If no scenario is present, the changes will be applied to the current scenario.
It is important that the Scenario name is uniquely qualified - if there are multiple scenarios with the same name, the full Scenario Path Name can be used. Scenario Path Names can easily be copied from AFT Impulse by right-clicking the scenario name and selecting "Copy Scenario Path Name."
Importing the File
When the sheet has been completely filled out, it can be imported from File -> Import Excel Change Data. When importing the data, the Object Change Log will appear, listing the changes that were made and any errors that occurred during the import.
Table 4: Excel Importing Error Messages
|
Error |
Description |
|
Scenario name is not unique in the model (use full scenario path name) |
There are multiple scenarios with this name. Use the fully qualified path name (e.g. Base Scenario\US Units\Pump A). |
|
Invalid change type |
The Change Code is not valid for the Parameter. For example, trying to change a string type with Change by Value (+/-). |
|
Invalid parameter ID |
The parameter given does not match the object type (e.g. Length for a junction). |
|
Invalid parameter value |
The value cannot be changed because the value is not valie. For example, a pump speed cannot be negative. |
|
Object not found |
A pipe or junction with the given ID was not found. |
|
Parameter conflict |
The value cannot be changed because it conflicts with another setting. For example, the loss value cannot be set when the junction is using a resistance curve. |
|
Scenario not found in the model |
No scenario by the given name was found in the model. |
Note: In order for the junction to accept the changes, some fields must already contain data. For example, if the control setpoint for a control valve is being changed, there must already be a setpoint and units entered into the control valve junction object. This is to ensure that the correct set of units are being used. These values can be set using Global Edit to an arbitrary value before the changes are made from Excel.
Related Topics
Importing Piping Component Files
Importing Caesar II Netral Files
Importing and Exporting EPANET Files
Related Blogs
Now it’s Super Easy! Changing Input Data in AFT Models using Excel Change Data
That was EASY! Quickly Change Pipe and Junction Input Data into AFT models using Excel Change Data



