Fluid Panel
The Fluid panel controls the properties of the fluid in the model. A default fluid is not selected - one must be defined to run any simulation unless one was previous defined on the Startup Window.
The first selection that must be made is what Fluids library to use. The available Fluid Libraries are:
-
AFT Standard - Common fluids from various industry standard sources have been curve fit to optimize calculation speed. This fluid library offers the best balance between accuracy and computation time. Saturation line data was added for AFT Standard fluids in xStream 2.
-
ASME Steam Tables - Properties are calculated via the Equations of State which were used to generate the classic steam/water tables in the IAPWS Industrial Formulation (1997). Saturation line data is included.
-
NIST REFPROP - The Reference Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties (REFPROP) Database is licensed from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) where properties for approximately 150 fluids are calculated via Equations of State. REFPROP supports user-specified fluid mixtures. For more info see the following sources: Program Summary, REFPROP FAQ, NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Chemical Name Search.
-
Chempak Fluid - Optional add-on for purchase which contains data for several hundred fluids and supports user-specified fluid mixtures. Chempak is licensed from Madison Technical Software.
-
User Library Fluid - If the desired working fluid is not available via the other sources, custom fluid properties can be entered and saved to the User Library for repeated use in the future. Fluids can be created using the Fluid Libraries menu.
Select a library by clicking the radio button next to the name of the library. After selecting a library, the Fluids Available in Library list is populated. One of the fluids can be selected and used with the Add To Model button.
Note: All fluids in xStream are treated as compressible and superheated as stated in the Engineering Assumptions.
When determining which fluid library is most appropriate, it is recommended that you consult the table below to ensure your selection suits your needs.
Table 1: Compatibility Chart for Fluid library Selection
| Fluid Library | Model Requirements | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixtures | Condensation Data | System Troubleshooting | Final Runs | Complex Systems* | |
| AFT Standard | ✔ | ✔** | ✔ | ||
| NIST REFPROP | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Chempak | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| ASME Steam | ✔ | ✔ | |||
* Evaluating the complexity of a system is most easily done in early runs of the model. It is suggested that all early runs use an AFT Standard fluid (even if the real system fluid is a mixture), and the run time recorded. This run time should inform your decision on which fluid library is needed to run the more polished runs when high accuracy results are needed. Run times can vary significantly between the 4 libraries, so make sure you evaluate your time constraints and accuracy needs when weighing this decision. Factors that can impact the run time include the ratio in the length of the smallest pipe to the largest pipe, presence of mixtures, usage of junctions containing resistance curve loss models, and the presence of sonic choking.
** It is strongly recommended that all runs used to troubleshoot the design of the system are run using AFT Standard.
The AFT Standard Library offers several equation of state models and enthalpy models. These models account for both temperature and pressure dependence on density and enthalpy.
Transport properties (specific heat, dynamic viscosity, and thermal conductivity) and Saturation Pressure are based on polynomial curve fits which are functions of temperature only. The assumption that these properties are only functions of temperatures is generally a good assumption at low pressure. However, at high pressures (especially above the Critical Pressure), this assumption starts to break down.
To add a fluid into your model, select it from the list at the top and choose the Add to Model button. The fluid will appear in the lower list of Fluids in Current Model. You can have only one AFT Standard fluid in your model, as there is no mixing support for Standard fluids.
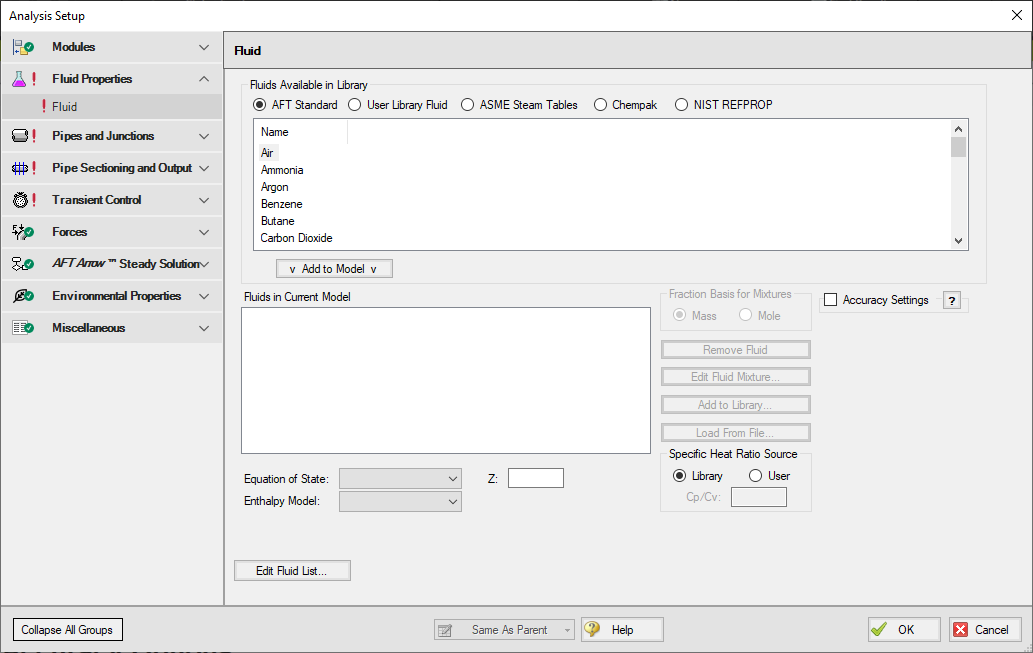
Figure 1: Fluid panel in Analysis Setup with the AFT Standard fluid library selected
Properties are calculated via the Equations of State which were used to generate the classic steam/water tables in the IAPWS Industrial Formulation 1997 for the Thermodynamic Properties of Water and Steam (ISPWS-IF97ASME Press, ASME International Steam Tables for Industrial Use (CRTD-Vol. 58), published by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Three Park Avenue, New York, NY 10016.), see ASME Press in References.
This library is selected by choosing the option ASME Steam Tables at the top of the Fluid panel. After this selection has been made, "ASME ’97 Steam" is displayed in the Fluids in Current Model area at the bottom of the Fluid panel.
Detailed fluid properties information from SteamCalc can be calculated using the AFT SteamCalc Viewer, which can be accessed from Tools > Fluid Property Viewers > SteamCalc. The SteamCalc Viewer will be launched as a separate application, which can then be used to calculate fluid properties at various conditions.
For more information on AFT SteamCalc Viewer see the SteamCalc Help File.
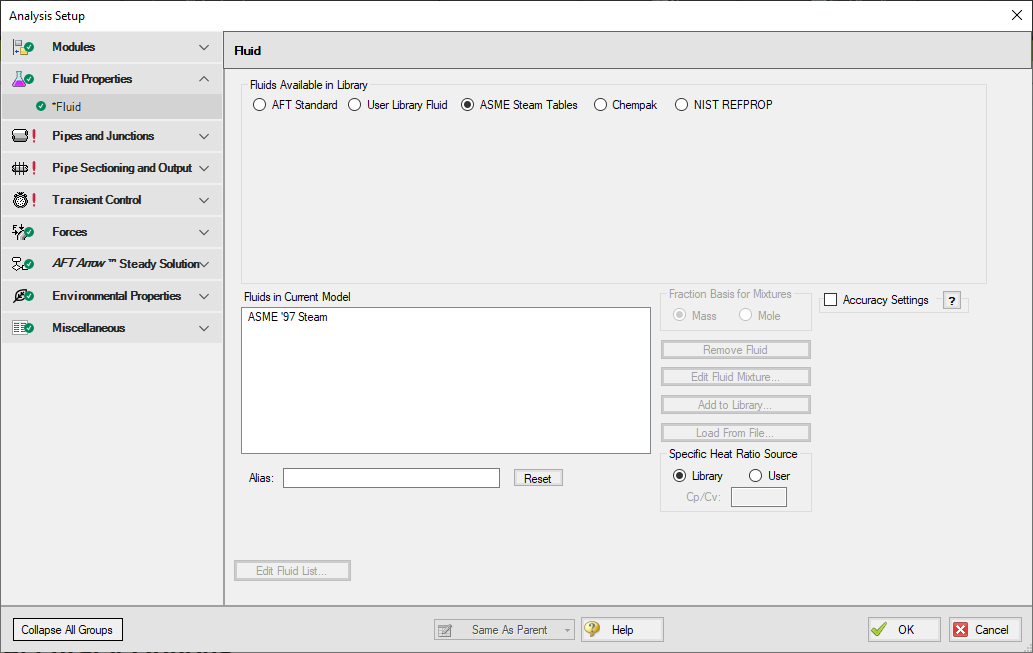
Figure 2: Fluid panel in Analysis Setup with the ASME Steam fluid library selected
The Reference Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties (REFPROP) Database is licensed from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) where properties for approximately 150 fluids are calculated via Equations of State (generally the Helmhotz Free Energy Equation of State). The data comes from Version 10 of the library. For more info see the following sources: Program Summary, REFPROP FAQ, NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Chemical Name Search.
A NIST REFPROP fluid can be added to the model in the Fluid panel by selecting the NIST REFPROP radio button. Add a fluid from the list by selecting it and clicking Add to Model, as shown in Figure 3.
The NIST REFPROP library allows for the calculation of gas mixtures, as well as dynamic mixing in the model, but note that no chemical reactions are modeled as listed in the Engineering Assumptions. Saturation line data is also available.
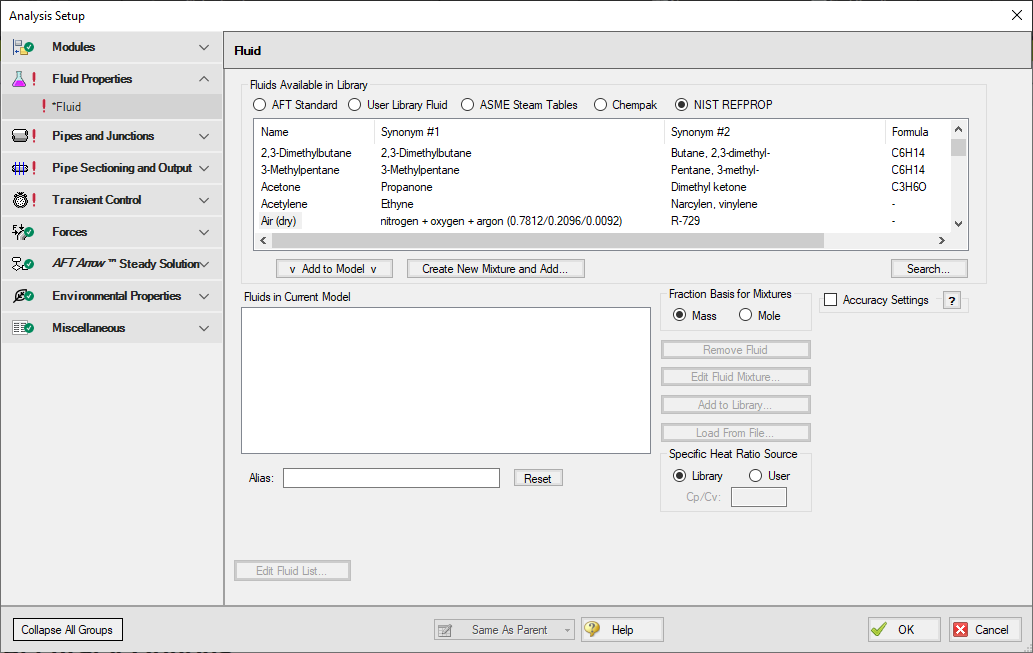
Figure 3: Fluid panel in Analysis Setup with the NIST REFPROP fluid library selected
Optional add-on for purchase which contains data for several hundred fluids. Chempak is licensed from Madison Technical Software.
Fluids from the Chempak library support gas mixtures and dynamic mixing, but no chemical reactions are modeled as listed in the Engineering Assumptions.
To add a Chempak fluid, select Chempak Fluid at the top of the Fluid panel. From here, select the appropriate fluid from the fluid list and click the Add to Model button. After a fluid is added to the model, it will appear in the lower list under Fluids in Current Model.
The equation of state is that of Wu & Stiel which is an extension of Lee Kesler to cover polars as well as non-polars. Properties are derived by interpolation between a Simple Fluid (mainly Argon), a Reference Fluid (mainly Octane) and a Polar Fluid (Water) using Acentric Factor and Stiel Y Factor as interpolating variables. These compound parameters (OM, the Acentric Factor, and YFACT the Stiel Y Factor) are derived from the compound vapor pressure curve. For more information see the Chempak Technical Information topic.
Detailed fluid properties information from Chempak can be calculated using the AFT Chempak Viewer, which can be accessed from Tools > Fluid Property Viewers > Chempak. The Chempak Viewer will be launched as a separate application, which can then be used to calculate fluid properties at various conditions. A Chempak Data license is required to use the Chempak viewer.
For more information on AFT Chempak Viewer see the Chempak Viewer Help File.
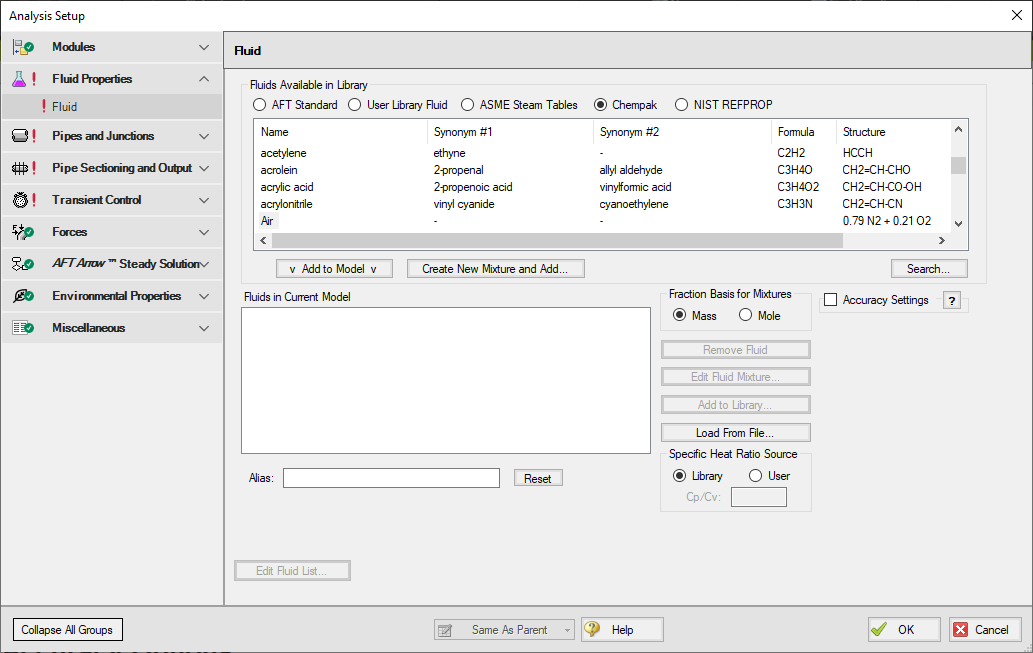
Figure 3: Fluid panel in Analysis Setup with the Chempak fluid library selected
Fluid Accuracy Settings
Several advanced settings are available to fine-tune the accuracy of the fluid property calculations and depend on which fluid library is selected. These settings are discussed in the Fluid Accuracy Settings topic.



