Fundamental Equations
The continuity equation applied to a constant area pipe yields:
|
|
(1) |
The one-dimensional momentum equation applied to a constant area pipe yields:
|
|
(2) |
Assuming the pipe is straight over the computing section, Figure 1 shows the relationship between dx and dz:
|
|
(3) |
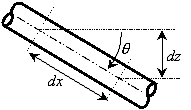
Figure 1: Relationship between distance along pipe (dx) and vertical elevation change (dz).
The fourth term on the left of Equation 2 accounts for pressure changes due to body forces. AFT xStream models body forces due to gravity. The default value of g in Equation 2 is the standard earth acceleration (i.e., 32.174 ft/sec2 or 9.81 m/sec2).
From the equation of state for a real gas:
|
|
(4) |
Related Topics
Review of Compressible Flow Theory
Pressure Drop in Pipes - Detailed Discussion
Extension of Single-Pipe Methods to Networks
Compressible Flow Theory in Single Pipes
Sonic Choking Detailed Description
Role of Pressure Junctions - Detailed Discussion (Long)



