Orifice Loss Model
Sharp-Edged Orifice
The orifice loss factors are all for turbulent Reynolds numbers. The sharp-edged orifice shown in Figure 1, is given by the following equation(Idelchik, 2007 Idelchik, I. E., Handbook of Hydraulic Resistance, 4th edition, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2007. , 259):
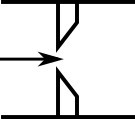
Figure 1: Sharp-edged orifice (in this case Aup = Adown)
Round-Edged Orifice with Different Upstream and Downstream Diameters
When the upstream and downstream pipe diameters are different for a round-edged orifice as shown in Figure 2, the round-edged orifice equation for different pipe areas is used and is given by the following (Idelchik, 2007 Idelchik, I. E., Handbook of Hydraulic Resistance, 4th edition, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2007. , 258)
where
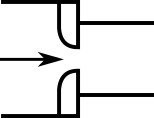
Figure 2: Round-edged orifice with different upstream and downstream pipe areas
Round-Edged Orifice with Identical Upstream and Downstream Diameters
When the upstream and downstream pipe diameters are the same for a round-edged orifice as shown in Figure 3, the round-edged orifice equation for the same pipe areas is used and is given by the following (Idelchik, 2007 Idelchik, I. E., Handbook of Hydraulic Resistance, 4th edition, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2007. ,262)
where
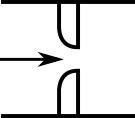
Figure 3: Round-edged orifice with the same upstream and downstream pipe areas
For other orifice configurations, see Chapter 4 of Idelchik's Handbook of Hydraulic Resistance (2007).
Other Loss Models
For information on the discharge coefficient loss model see the Discharge Coefficient Loss Model topic. For information on the orifice loss when the flow is choked see the Sonic Choking description.



