Iterations Panel
Relaxation, iteration limits, and matrix method settings are defined on the Iterations panel in Analysis Setup. Most settings on this panel will not affect the final result. The default state of the Iterations panel is shown in Figure 1.
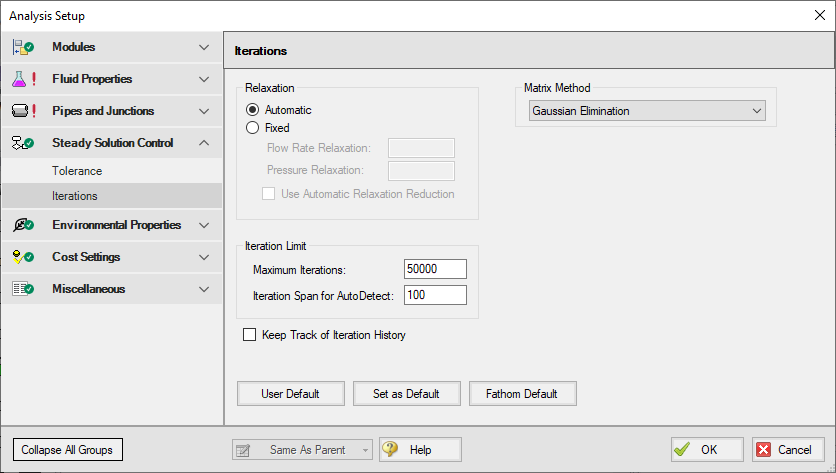
Figure 1: Iterations panel in Analysis Setup
Relaxation
Relaxation slows iterative progress toward a solution reducing the destabilizing effect of non-linear systems.
-
Automatic - Implements an adaptive relaxation scheme that reduces the relaxation dynamically in response to highly non-linear features of the problem.
-
Fixed - Allows for user specified Flow Rate and Pressure Relaxation
When applied to the flow solution, relaxation r is used as follows:
A relaxation of 1 is the same as no relaxation. Each iteration's prediction is used directly in the next iteration.
A relaxation of 0 is not allowed, as this would prevent the parameter from changing.
-
Flow Rate Relaxation - For highly non-linear systems, a flow rate relaxation of 0.1 is advised. Experience shows that using flow rate relaxation factors between 0.5 and 1 has limited usefulness. If a flow rate relaxation of 1 does not work, you should generally try flow rate relaxation parameters between 0.1 and 0.5. In more extreme cases, a flow rate relaxation factor smaller than 0.1 may be required.
-
Pressure Relaxation - Because of the nature of the matrix solver, experience indicates that if pressure relaxation is used, it should always be set to 0.5 or 1 to maintain stability.
Iteration Limit
-
Maximum Iterations - 50000 by default, sufficient for the vast majority of models. Most models converge in a relatively small number of iterations. This limit does not directly affect the solution.
-
Iteration Span for AutoDetect - 100 by default, if the Solver detects that no meaningful progress has been made to convergence within this many iterations, relaxation is automatically lowered. This also automatically adjusts tolerance.
Matrix Method
Network analysis requires solving complex matrices potentially thousands of times. Different methods may solve faster or slower, but have no bearing on results. The default method of Gaussian Elimination is highly robust and usually provides the fastest convergence. The available Matrix Methods are:
-
Gaussian Elimination
-
Gaussian Elimination With Pivoting
-
LU Decomposition
Iteration History
Iteration History shows a history of which pipe or junction is most out of tolerance, which is helpful for troubleshooting. After enabling Iteration History on the Iterations panel in Analysis Setup, the Iteration History can be viewed from the Solution Progress window by pausing the calculation and selecting the Other Actions button.



