Fundamental Equations
Conservation of Mass - The continuity equation applied to a constant area pipe yields:
|
|
(1) |
Conservation of Momentum - The one-dimensional momentum equation applied to a constant area pipe yields:
|
|
(2) |
Conservation of Energy - The First Law of Thermodynamics applied to compressible flow with stagnation enthalpy yields:
|
|
(3) |
The Equation of State for a Real Gas:
|
|
(4) |
Assuming the pipe is straight over the computing section, Figure 1 shows the relationship between dx and dz:
|
|
(5) |
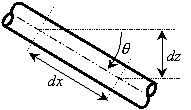
Figure 1: Relationship between distance along pipe (dx) and vertical elevation change (dz)
The fourth term on the left of Equation 2 accounts for pressure changes due to body forces. xStream models body forces due to gravity. The default value of g in Equation 2 is the standard earth acceleration (i.e., 32.174 ft/sec2 or 9.81 m/sec2).