Verification Case 2
PRODUCT: xStream
TITLE: XtrVerify2.xtr
REFERENCE: Moody, Frederick J., Introduction to Unsteady Thermofluid Mechanics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY, 1990, Page 452-453, Example 8.5, Figures 8.16 & 8.17
FLUID: Air
ASSUMPTIONS: Calorically perfect gas, friction is negligible
RESULTS:
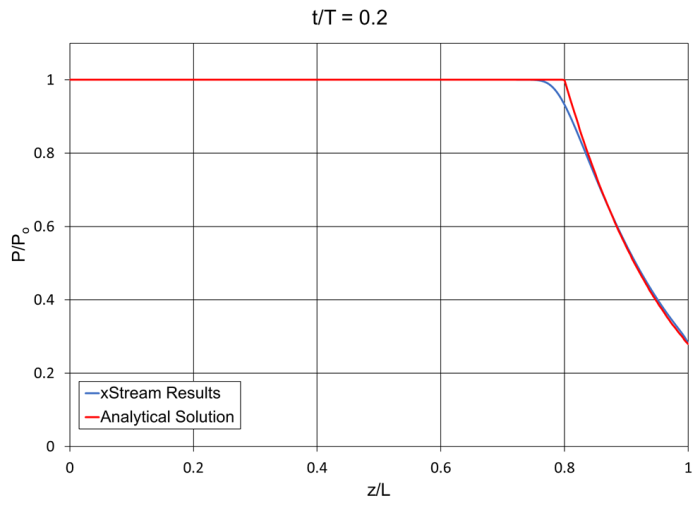
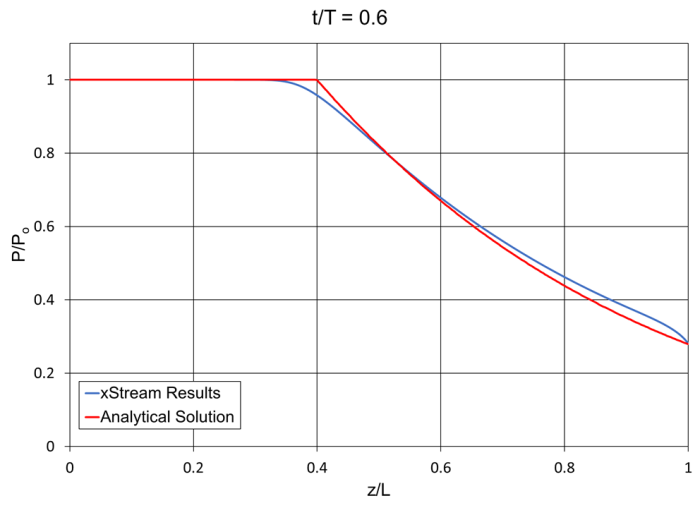
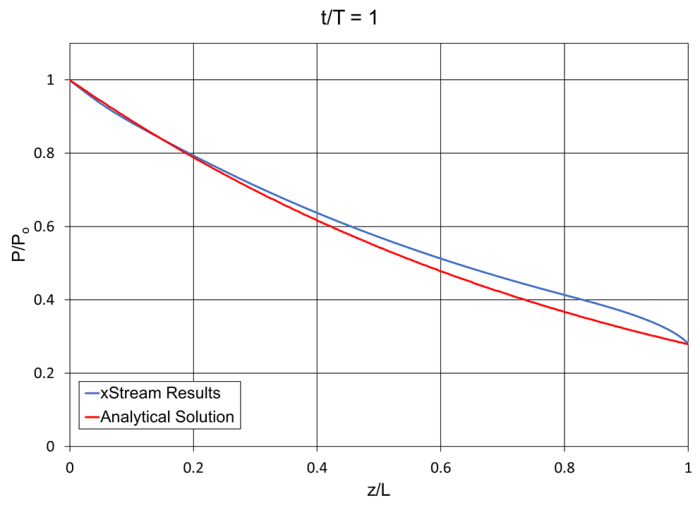
Note: The xStream Standard library fluid for air was updated in xStream 3, which may cause some results to differ from those obtained in previous versions.
DISCUSSION:
To find an analytical solution for this example Moody assumes the process is adiabatic, the pipes are frictionless, and that the fluid is ideal and calorically perfect. The assumptions made by Moody allow an isentropic solution to be found for the expansion wave.
The tube rupture is modeled as an instantaneous drop in static pressure based on the dimensionless static pressure drop ratio in Moody Figure 8.16, P/Po.
Though Moody assumes that the pipes are frictionless, the pipes in xStream are instead defined as hydraulically smooth. This is done to prevent supersonic flow in the xStream model.
The difference in friction models and the fact that the fluid in xStream is not modeled as calorically perfect can account for the minor differences between the xStream results and the analytical solution.