Centrifugal Compressor
Centrifugal Compressor Curve
A Compressor Curve is required to model a centrifugal compressor. This is the typical Head or Pressure vs. Flow information that will be available from any compressor manufacturer.
To enter these curves, click Enter Curve Data. Once this data has been defined, previews of the applied curves can be seen here.
Note: AFT xStream does not have a means to account for stall or surge lines for the compressor. Therefore, it is possible that xStream will allow the compressor to operate at unrealistic conditions. It is advised that the user check the results to ensure that the compressor did not reach the surge or stall lines during the run, design alerts can be useful to assist with this check.
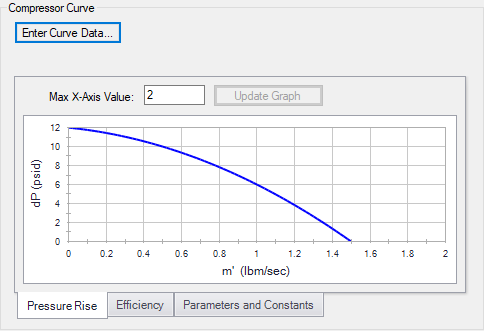
Figure 1: Standard Compressor Curve
Added Pressure
If the compressor curve is entered using pressure rise information as opposed to a head rise, the pressure rise will need to be specified as either a stagnation or static pressure. This specification is performed on the Compressor Model tab under the Centrifugal Compressor specification. Note that mechanical energy rises are typically entered in xStream as pressure rises instead of head rises because the usefulness of the head term in variable-density systems is diminished.
Compression Process Thermodynamics
In xStream the compressor will always be modeled as isentropic and 100% efficient. If the compression process is isentropic, the temperature rise is given by the following isentropic relationship:
Note that these pressures and temperatures are static and not stagnation. Gamma is the isentropic expansion coefficient or specific heat ratio, depending on the Fluid Accuracy Options.
Note: The Compressor Configuration window provides the option to enter efficiency option for the sole purpose of maintaining input when models are imported from other AFT products. The compressor efficiency data will not be used for calculation purposes.



